| Title | A two-step chemical mechanism for ribosome-catalysed peptide bond formation. |
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2011 |
| Authors | Hiller DA, Singh V, Zhong M, Strobel SA |
| Journal | Nature |
| Volume | 476 |
| Issue | 7359 |
| Pagination | 236-9 |
| Date Published | 2011 Jul 17 |
| ISSN | 1476-4687 |
| Keywords | Biocatalysis, Catalytic Domain, Kinetics, Models, Biological, Models, Chemical, Models, Molecular, Organelle Biogenesis, Protein Biosynthesis, Ribosomes, Static Electricity |
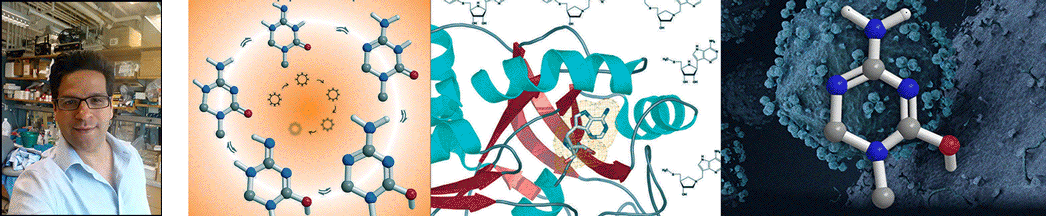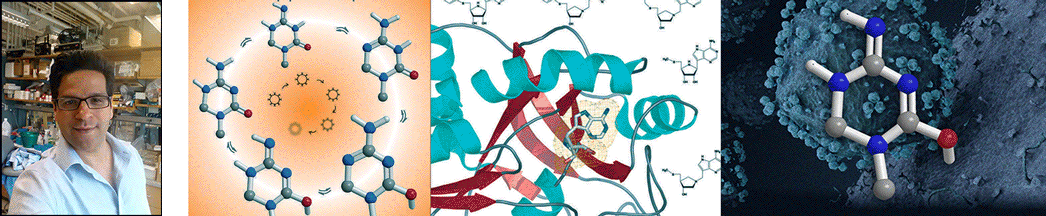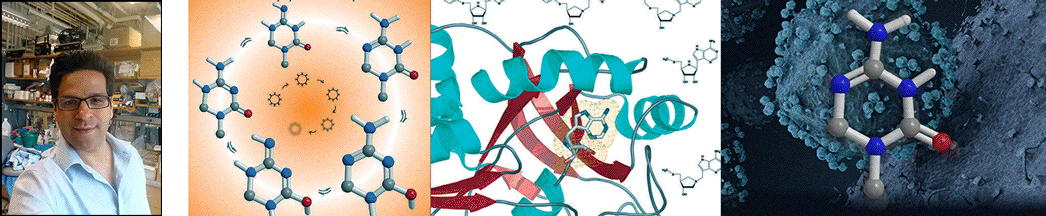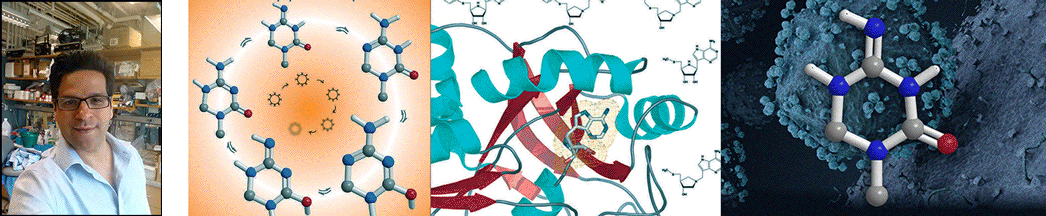
| Abstract | The chemical step of natural protein synthesis, peptide bond formation, is catalysed by the large subunit of the ribosome. Crystal structures have shown that the active site for peptide bond formation is composed entirely of RNA. Recent work has focused on how an RNA active site is able to catalyse this fundamental biological reaction at a suitable rate for protein synthesis. On the basis of the absence of important ribosomal functional groups, lack of a dependence on pH, and the dominant contribution of entropy to catalysis, it has been suggested that the role of the ribosome is limited to bringing the substrates into close proximity. Alternatively, the importance of the 2'-hydroxyl of the peptidyl-transfer RNA and a Brønsted coefficient near zero have been taken as evidence that the ribosome coordinates a proton-transfer network. Here we report the transition state of peptide bond formation, based on analysis of the kinetic isotope effect at five positions within the reaction centre of a peptidyl-transfer RNA mimic. Our results indicate that in contrast to the uncatalysed reaction, formation of the tetrahedral intermediate and proton transfer from the nucleophilic nitrogen both occur in the rate-limiting step. Unlike in previous proposals, the reaction is not fully concerted; instead, breakdown of the tetrahedral intermediate occurs in a separate fast step. This suggests that in addition to substrate positioning, the ribosome is contributing to chemical catalysis by changing the rate-limiting transition state. |
| DOI | 10.1038/nature10248 |
| Alternate Journal | Nature |
| PubMed ID | 21765427 |
| PubMed Central ID | PMC3154986 |
| Grant List | R01 GM054839-13S1 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839-12 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839-12S1 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839-10 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States GM54839 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839-13 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States R01 GM054839-11 / GM / NIGMS NIH HHS / United States |
A two-step chemical mechanism for ribosome-catalysed peptide bond formation.
Submitted by Anonymous (not verified) on